To further compare CRISPRi with CRISPRn, we targeted
another pluripotency transcription factor,
OCT4
, with two in-
dependent gRNAs. Similar to our findings with
NANOG
,
OCT4
mKate2
CRISPRi
NANOG+DAPI
500
µ
m
NANOG
mKate2
NANOG
+DAPI
500
µ
m
CRISPRn
NANOG
Count
NANOG
d12
d7
d6
d5
d2
d3
d4
d0
d1
Count
NANOG
d12
d7
d6
d5
d2
d3
d4
d0
d1
A
Total=14
Total=30
Total=27
+ Dox (day 12)
+ Dox (day 17)
Total=14
Total=30
Total=27
Total=44
Total=13
Total=33
+ Dox (day 12)
+ Dox (day 17)
Total=44
Total=33
Total=13
B
E
G
F
H
NANOG+DAPI
NANOG+DAPI
NANOG+DAPI
NANOG+DAPI
DAPI
DAPI
DAPI
DAPI
NANOG
NANOG
NANOG
NANOG
NANOG
g+358
mKate2
mKate2
mKate2
mKate2
NANOG+DAPI
NANOG+DAPI
NANOG+DAPI
NANOG+DAPI
DAPI
DAPI
DAPI
DAPI
NANOG
NANOG
NANOG
NANOG
mKate2
mKate2
mKate2
mKate2
NANOG
g+358
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 12
Fibroblast
+ Dox
NANOG
GAPDH
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 12
Fibroblast
+ Dox
NANOG
GAPDH
C
No mutation
In frame INDEL
Out of frame INDEL
No mutation
In frame INDEL
Out of frame INDEL
D
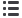
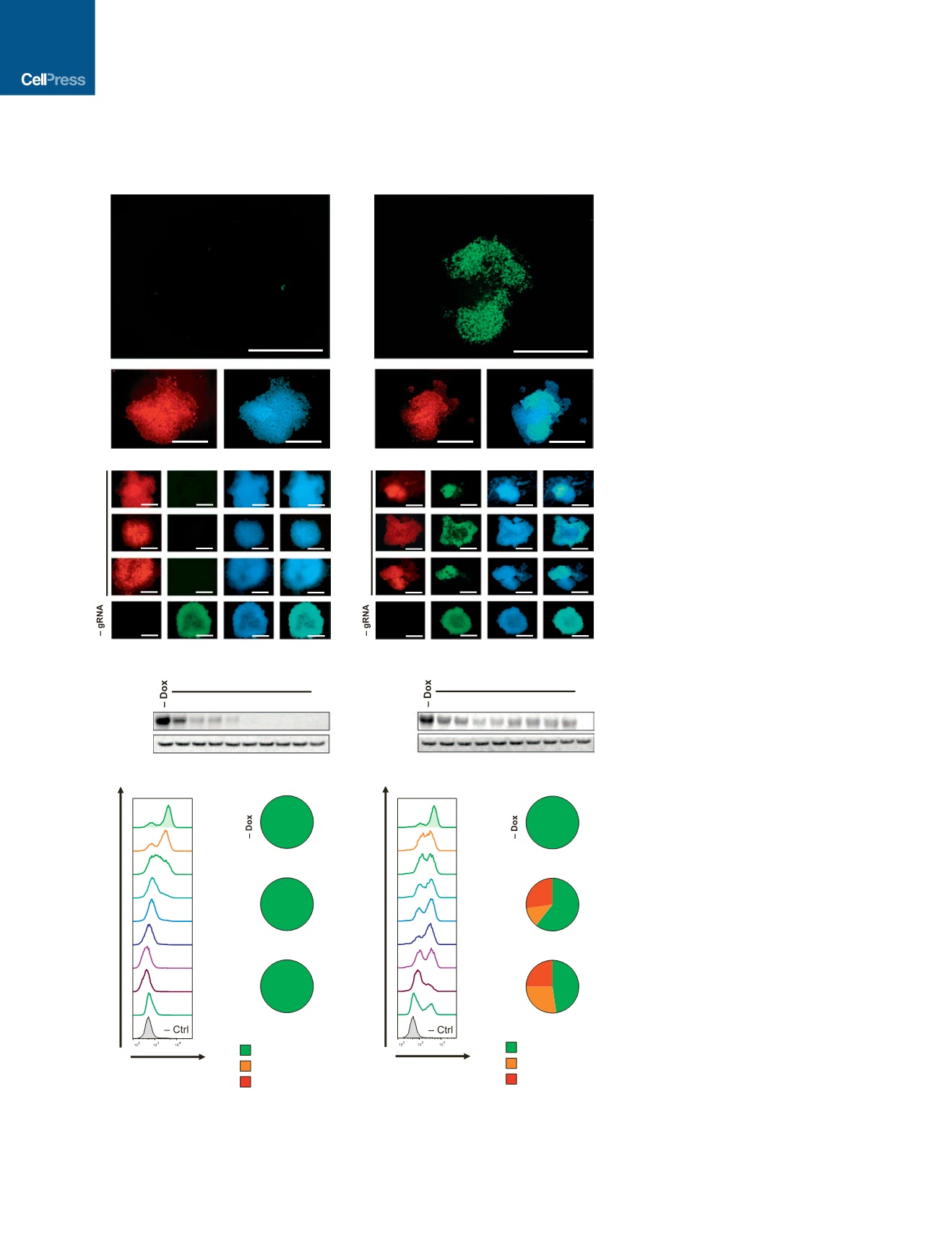
Figure 2. Comparison of the Efficiency
of CRISPRi Knockdown and CRISPRn
Knockout
(A and B) Immunostaining of representative (A)
CRISPRi and (B) CRISPRn stable clones, each
containing the same gRNA targeting the first exon
of
NANOG
(
NANOG
g+358). After 7 days of doxy-
cycline treatment,
NANOG
expression (green) was
completely lost in all CRISPRi clones but showed
a variegated pattern of knockout in multiple inde-
pendent CRISPRn clones. The mKate2 signal in-
dicates the presence of the gRNA-expression
vector in all cells within the clone. Nuclei are
counterstained with DAPI.
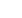
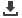
(C, D, E, and G) Western blot and flow cytometry
analyses of (C and E) CRISPRi and (D and G)
CRISPRn stable clones that contain the same
gRNA against the first exon of
NANOG
. With
CRISPRi,
NANOG
expression was uniformly
decreased during doxycycline treatment and did
not increase thereafter; however, with CRISPRn,
the percentage of NANOG-positive cells fluctu-
ated during doxycycline treatment. Even after
12 days of continuous doxycycline treatment,
30% of the population stained positive for
NANOG.
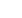
(F and H) Genomic DNA was extracted from (F)
CRISPRi and (H) CRISPRn stable lines containing
a gRNA against
NANOG
before and after contin-
uous doxycycline treatment for up to 17 days
and subjected to sequencing. Red, out-of-frame
INDELs; orange, in-frame INDELs; green, non-
mutated alleles. Even after 12–17 days of
continuous doxycycline treatment, 50%–70% of
sequenced alleles from CRISPRn contained no
mutation, and 30%–50% of mutated alleles were
in-frame INDELs. No mutations were observed in
either CRISPRi or CRISPRn without doxycycline,
and the CRISPRi clones did not contain any
mutations after doxycycline treatment. The total
number of sequenced colonies is listed below
each pie graph.
Scale bars, 500
m
m.
was completely knocked down in inde-
pendent CRISPRi clones expressing the
gRNA vector after doxycycline treatment
(Figure S3E). In contrast, the attempted
knockout of OCT4 with CRISPRn again
yielded incomplete effects (Figure S3F).
These findings were also replicated in
a completely different iPSC line (WTB
genetic background; CRISPRi Gen1B
and CRISPRn Gen1B) (Figures S1D and
S1F). We analyzed the genomic DNA of
CRISPRn cells after 14 days of contin-
uous doxycycline treatment and found
30%–40% of the mutated alleles had in-
frame INDELs (a total of 91 sequenced
clones) (Figure S3G). These results sug-
gested that, in the context of targeting pluripotency factors,
CRISPRi more rapidly generates loss-of-function phenotypes
in bulk populations than CRISPRn. CRISPRi caused a complete
544
Cell Stem Cell
18
, 541–553, April 7, 2016
ª
2016 Elsevier Inc.